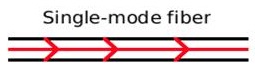
Fiber is divided into single mode and multimode. Contrary to what you would think, single mode is better, and can carry coherent information longer than multimode fiber.

Single mode has a glass optic path that is narrow enough that light is directed down that path without reflecting off the outside surface of the glass stand. Multimode means that light is repeatedly reflecting off the sides at various rates. The more reflections a beam of light undergoes mean a longer total path than light that sticks to the center of the glass. Some wavelengths and light rays encounter more reflections than others. This means that over long distances, packets of light can become compressed together, making it impossible to discern the data patterns that the light represents.
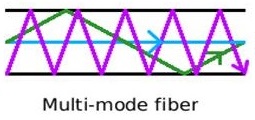
Multimode fiber has a maximum distance of up to 3000 feet. S ingle Mode Fiber has a maximum distance of up to 25 miles (40Km). Glass has greater distance, but copper is less expensive.
Fiber also has two common connector types:

S T (Straight Tip) Connector優eveloped by AT&T, this uses a BNC attachment mechanism which is popular, but mainly for multimode fiber.

S C (Subscriber or Square) Connector佑onnectors are latched, so this works for either SMF (single mode) or MMF (multi mode). Good for 1000 matings.
Another type:

L C (Local Connector)祐mall form factor, popular for Fibre-Channel and Gigabit Ethernet adapters. This connector is replacing SC connectors because of its smaller form factor.
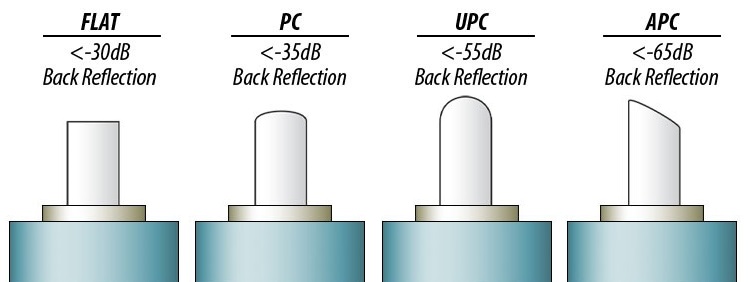
Many connectors are Angle-Polished Connectors (APC). These are generally distinguished by some green on the connector. They have the fiber end face polished at an angle that prevents light reflecting back from its surface of the fiber strand it is facing to reverse back down the fiber strand it just traveled. This is known as insertion loss. Any optical reflections can reduce the distance that the light can travel.
Hybrid Fiber Coaxial (HFC) is a telecommunications industry term for a network that incorporates both optical fiber and coaxial cable to create a bandwidth network.