29.97 = Frame rate adopted for color television – See 59.94
16:9 = The aspect ratio used for widescreen television 16 = width, 9 = height. Just to add to your confusion, if you work the math, 4:3 is actually 16:12.
2K = Similar format to HD, but slightly wider aspect ratio, used in digital cinema
3/2 pull down = early scheme developed to convert motion picture film shot at 24 frames-per-second to televisions 30 frames per second. Every third film frames is repeated to equal televisions 30. This creates a subtly discernable judder effect that most people recognize as the look of film not video. Converting to 30 fps allows the existing broadcast infrastructure to handle film or video shot in 24 fps like any other video signal, even intercutting cameras.
4:3 = The aspect ratio used for conventional television
4K = Picture format with four times the number of pixels than High Definition 1080p.
5D = 3D and 2D production done out of the same production truck. The left eye of the 3D picture is used for the 2D picture.
720/1080 = Number of lines in an HD television picture. Also, see spatial and temporal resolution. FOX, ESPN, ABC, Disney networks and the Department of Defense operate in 720p, all other networks including CBS, NBC and PBS operate in 1080.
8K = Picture format with eight times the number of pixels of HD.
9 PIN D = common connector used for serial data on broadcast equipment. Comes in male & female versions
24P = 24 is the frame rate in motion picture production in the U.S. P stands for progressive scan. In order to make video look more like filmed material, producers often ask to shoot in 24P. 25P is the standard in European countries. In truth, 24p video is almost always shot in the 23.98 legacy NTSC frame rate, unless being intercut with film. See also 3/2 pull down.
A1 = Person responsible and in charge of the audio effort. Usually the A1 is the person who mixes the show.
A2 = This person works for the A1 and is generally responsible for all audio setup outside of the truck.
A-game = The nationally television network game. Usually applies to NFL Sunday games. This is the game that markets without regional games to air will air. More equipment nd more predominant talent will be devoted to this game.
ABC = In Australia the Australian Broadcasting Corporation. In the UK ABC Weekend TV, a former ITV broadcaster. In the US, American Broadcasting Company, a television and radio network originally spun off of the NBC network in the 1940s.
Ace = 1000 watt spotlight
Active = As opposed to passive, this means that electronic or electric circuitry is involved in accomplishing something.
Active Video = the part of the video stream that actually gets displayed. For SD that’s 720 pixels horizontally by 480 vertical lines.720p is 1280x720, 1080 (both i and p) is 1920x1080. See temporal resolution for the difference between 1080i and 1080p.
AD = Assistant Director, as the names implies, Directors assistant. Generally keeps track of time while on air , counts in and out of breaks and recorded segments. Usually. The one in the truck constant communications with the Broadcast during a live show.
A/D = Analog/digitalconversion
ADAM = Advanced Digital Audio Matrix. An intercom matrix made by RTS / Telex common in most mobile units.
ADC = Analog-to-digital converter
ADDER = an early system manufactured by Telecast Fiber for the transport of audio signals over fiber cabling.
AES = Audio Engineering Society
AFD = Active Format Descriptor
Aircheck = The recorded copy of a broadcast. This can be a digital or analog recording.
All 22 = Camera that keeps a wide shot of all 22 football players on the field.
Analogue = Contrary to digital continuously variable signal, circuit or device.
Analog recording = Recording of audio using an electronic signal that varies continuously. The main drawback of analog recording is the introduction of inherent noise to the recorded signal.
Analog transmission = The broadcasting of a signal using an analog recording. Examples of use include radio.
Anchor Element = Audio component used by Dolby to determine what to set loudness values to if dialog is not present in a scene.
Anchor Frame = In compression a video frame that stands on its own, it doesn’t need other frames to decode it.
AP = Asscoiate Producer or Assistant Producer
API = Application Programming Interface. Software calls available for application level programs to call routines and use services of software running underneath. Can be application software calling another or a higher level software program calling services from the Operating System. A common use is that of high level programs calling the set of API in Windows known as sockets to access networking services.
Apple Box = nicely made closed wooden box 2’ x 1’ x 8” high, usefully to raise height, compensate for a stair, sit on or anything else handy. Also comes in half height, a half Apple, or quarter height, a quarter Apple, Adopted from the film industry where it can general be found in Grip trucks.
ARC = Aspect Ratio Converter
Archive = May refer to the following:
* Storage of master material under controlled conditions
* Long term storage of material on an storage medium.
* Archive copy is a master copy intended solely for storage and not to be used in distribution.
Artifacts = Noticeable loss of video and/or audio fidelity in a broadcast or recording caused by limitations in the technology used. Usually reflects undesirable distortion(s) of the original when digitized.
ARC Aspect Ratio Conversion = Changing the original aspect ratio of a HD picture through down conversion to either 16:9 letterbox or 4:3 center cut (see Center Cut)
Asynchronous serial interface = a streaming data format which often carries an MPEG transport stream
Aspect ratio = the ratio between the width and the height of the picture. In NTSC television sets, this is 4:3; in widescreen (ATSC) sets, 16:9. Sometimes it is printed decimally as 1.33:1 for 4:3 and 1.78:1 for 16:9, >universal to high-definition and digital television.
ATM = Asynchronous Transfer Mode
ATR = Audio tape recorder, a method of recording sound by electromagnetic pulses on a sensitised plastic strip
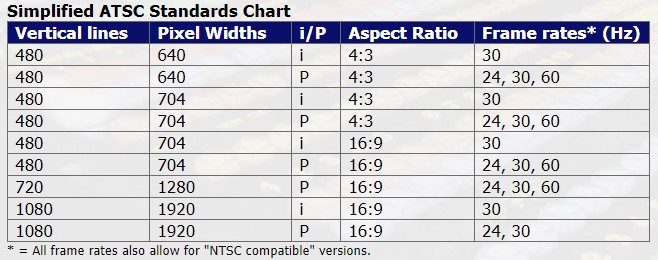
ATSC = Advanced Television Systems Committee. A committee established by the FCC to decide the technical standards for digital broadcasting in the US.
Aerial shots = are usually done with a crane or with a camera attached to a special helicopter to view large landscapes. This sort of shot would be restricted to exterior locations.
Audience = a group of people who participate in a show or encounter a work of art, literature, theatre, television music or academics in any medium.
B
B Game = Usually a regional game, usually referred to in context with the NFL. There can be multiple B games.
B-roll = supplemental or alternate footage intercut with the main shot in an interview or documentary.
B Unit = Second trailer that travels with the main “A Unit”. The B unit handles operations and equipment overflow from the A Unit. Often Graphics or replay will be moved off to the B Unit. Other utility functions are off loaded to the B Unit. Often the B Unit will carry Chapman camera dollies or other camera platform accessories. Quite often the B Unit will be setup as a “Sandbox”.
Backhaul = The process of sending video and audio from a remote site back to a network or a local station. Usually via satellite, microwave, or fiber landlines.
Balanced Audio = Audio that is differently driven down a path, where neither lead of the audio pair is at ground potential. Each signal on the two leads is 180 degrees out of phase with each other. Because of this fact balanced audio is generally immune to outside interference. Audio XLR connectors have three conductors, two for each of the two audio signals and one for ground. Compared to single ended audio where the audio signal is on a single conductor and referenced to ground, which is the other conductor. RCA audio connectors carry single ended audio.
Bandwidth = the available space between two given points on the electromagnetic spectrum and, inter alia, the amount of information that can be squeezed into that space.
Barn Door = adjustable device fitted to the front of a lighting fixture to cut off light spill as necessary
Baseband = Video and audio that has not been compressed or modulated onto a RF carrier.
Basic Interoperable Scrambling System = usually known as BISS. satellite signal scrambling system developed by the European Broadcasting Union and a consortium of hardware manufacturers.
BBC= British Broadcasting Corporation .The main public service broadcaster in the
Bed = A production audio element, usually instrumental music or sound effect played in the background of a spoken commercial, promo or other announcement.
Belly Bay = storage areas along the lower portion of a mobile unit used to carry cameras, cable and other items needed on a remote. The A/C power entrance and signal connections are often located in belly bays. Also known as Bunkers.
Beltpack = small interface box for intercom or IFB, has appropriate volume control and talk switches as needed.
Bias = A constant amplitude high frequency signal added to the recording signal to improve the Signal_to_noise_ratio and reduce the distortion of an analog tape recording.
Billboard = A short announcement to identify a sponsor at the beginning or end of a production element such as the news or traffic/weather reports.
Bird = Slang for a satellite
Black Burst = composite video signal, with a black picture used to synchronize (Genlock) certain video equipment together, thereby aligning the output. The signal is made up of vertical and horizontal sync. and Chroma burst information (1 wire).
Blu-ray = an optical disc storage medium designed by Sony to supersede the standard DVD format. Its main uses are for high-definition video and data storage with 50GB per disc. The disc has the same physical dimensions as standard DVDs and CDs.
Bologna Slicer = Manual hand crank on a camera for controlling the focal length of the lens.
Bookable Facilities = Technical or production services, facilities or equipment available to Broadcast Partners.
Booth Kit = All the microphones, headsets, and cables used at the announcer’s position or booth in one box, case, or kit.
BNC = British Naval Connector, connector found on most coax cables.
Breakbumper = UK: An animation or logotype briefly shown after the end of a program or part of a program before the advertising.
Breaking news = Interruptions of regular or planned programming for recently-occurring events as reported by a news organization or agency.
Breakout Box = A box with multiple connectors on it that is connected to a cable that encompasses multiple feeds within it. The breakout box provides a separate connector for each of the individual feeds for the signals in the cable. See mults and pigtails.
Broad = lighting instrument with a wide rectangular beam, usually without a lens.
Broadcast Center = the networks headquarters. Usually signals go from the mobile unit to the Broadcast Center for commercial integration, quality control and then distribution.
Broadcasting = the distribution of audio and/or video signals which transmit programs to an audience. The audience may be the general public or a relatively large sub-audience, such as children or young adults.
Broadcast Compound = A specific area at a venue designated for the parking and operation of mobile technical and production trucks, office trailers and other vehicles.
Broadcast Area or range (viewing range for TV) = the service area that a broadcast station or other transmission covers via radio waves (or possibly infrared light, which is closely related). It is generally the area in which a station's signal strength is sufficient for most receivers to decode it, however this also depends on interference from other stations.
BTA = Black To Air
BTU (British Thermal Unit) = Measure of heat. 12,000 BTU/hr equals 1 ton of cooling. 3,515 watts of electrical power generates 12,000 BTU/hr of heat.
Bug = A permanent on-screen logo. Usually located in the corner of the screen. So-called because it looks like an insect is hanging out in the corner of the screen.
Bumper or Bump = An element that acts as a transition to or from commercial breaks.
Bumper Music = A pre-recorded production element containing voice-over and/or music that acts as a transition to or from commercial breaks.
Bus = Circuitry that transports multiple digital signals grouped together as parallel lines. Also refers to large conductors used to carry electric power.
C
C band = a name given to certain portions of the electromagnetic spectrum, as well as a range of wavelengths of microwaves that are used for long-distance radio telecommunications. The IEEE C-band - and its slight variations - contains frequency ranges that are used for many satellite communications transmissions; by some Wi-Fi devices; by some cordless telephones; and by some weather radar systems. For satellite communications, the microwave frequencies of the C-band perform better in comparison with Ku band (11.2 GHz to 14.5 GHz) microwave frequencies, under adverse weather conditions, which are used by another large set of communication satellites.
Cable news = television channels which are devoted to current events 24 hours per day.
Cable Television = a system of providing television to consumers via radio frequency signals transmitted to televisions through fixed optical fibers or coaxial cables as opposed to the over-the-air method used in traditional television broadcasting (via radio waves) in which a television antenna is required. FM radio programming, high-speed Internet, telephony, and similar non-television services may also be provided. The abbreviation CATV is often used to mean Cable TV.
Call Letters = The official name of the radio/television station in the USA. Also known as a station's call sign. Originally call letters were based on ship call signs as originally radio stations were primary concerned with ship-to-shore two way communications. Shore radio stations east of the Mississippi were west of ships in the Atlantic and thus were given call letters starting with “W”. Shore stations west of the Mississippi were given call letters starting with “K”. The Mississippi rule wasn’t always followed, hence stations like KDKA in Pittsburg and KYW in Philadelphia. It should be noted that KYW started life near the Mississippi and gradually migrated east.
Calling the Show = The director giving instructions during the production of a show.
Calm Commercial Advertisement Loudness Mitigation Act) = The FCC now requires that broadcasters be held responsible when viewers believe they are being abused by audio volumes varying all over the map. Why all these problems with varying levels? Signals with a small peak-to-average ratio and peaks near full level have a high average, which make them sound very loud. Historically this is what commercial producers wanted, in order to reach out and grab the viewer. Thus audio was compressed; the dynamic range was reduced to achieve this effect. Another issue is that if left unprocessed, music has a wider dynamic but a lower average level, while dialogue normally has less dynamic range. So when music sound levels were brought up historically, somewhere in the process, compression would kick in.
Cam-lock = twist connector that creates a slight scraping action that cleans the mated surfaces with each use.
Cans = Slang for Headphones
Category 3 cable, commonly known as Cat 3 = an unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable designed to reliably carry data up to 10 Mbit/s, with a possible bandwidth of 16 MHz.
Category 5 cable = a twisted pair high signal integrity cable type often referred to as Cat5.
CBS (Columbia Broadcasting System) = an American television and radio network.
CBR = constant bit rate
CCIR Comité consultatif international pour la radio = In English, "International Radio Consultative Committee", the organisation responsible for assigning frequencies to radio stations between 1927 and 1992. Now known as ITU-R
CEA = Consumer Electronics Association in the U.S.
Channel = a range of frequencies (or, equivalently, wavelengths) assigned by a government for the operation of a particular television station or radio station. In common usage, the term also may be used to refer to the station operating on a particular frequency.
Character Generator, often abbreviated as CG = a device or software that produces static or animated text (such as crawls and rolls) for keying into a video stream. Modern character generators are computer-based, and can generate graphics as well as text. (The integrated circuit, usually in the form of a PROM, that decodes a keystroke in a keyboard, and outputs a corresponding character, is also referred to as a "character generator."
Chroma Key = The keying of video over existing video based on the color. Often used on weather sets where the map is keyed over a blue or green background. While the newly keyed video appears behind the weathercaster it is in reality keyed over the background.
Clamshell Access – A production trailer designed so that the outside side panels of the trailer open up to provide access to the rear racks. Usually this access if only on the street side of the trailer as a long row of racks against that wall, through the length of most of the truck are installed. This long row of racks usually comprises the monitor walls in the production compartments and the replay and graphics compartments, along with some of the transmission area racks.
Closed-circuit television CCTV) = the use of video cameras to transmit a signal to a specific place, on a limited set of monitors.
Close-up = as used television, and still photography to tightly frame a person or an object. Close-ups are one of the standard shots used regularly with medium shots and long shots. Close-ups display the most detail, but they do not include the broader scene. Moving in to a close-up or away from a close-up is a common type of zooming.
Clean Feed = A video feed without any graphics overlaid and usually with only natural sound audio.
Clip = Short programming segment used in a larger program.
Closed Captioning = Text version of a programme's dialogue, overlayed on the screen by an equipped television set for the hearing impaired.
Clutter = An excessive number of non-programm elements (such as commercials) appearing one after another.
= an electrical cable with an inner conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer typically of a flexible material with a high dielectric constant, all of which are surrounded by a conductive layer (typically of fine woven wire for flexibility, or of a thin metallic foil), and finally covered with a thin insulating layer on the outside. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis.
Cobra = device made by Telecast fiber to convert triax cable transmission between the camera head and base station from triax to fiber and back. Used on very long runs of cable beyond the reach of triax.
Cobranet = multichannel audio transport scheme using Ethernet protocols.
CODEC = n acronym of Compression, Decompression = a device or piece of software which takes one file or signal format and translates it to another with an ideally undetectable loss of quality. Equipment that takes baseband video and audio and compresses it into one of many file or transport stream formats or decompresses it back to baseband.
Color = a type of television test pattern, and is most commonly used in countries where the NTSC video standard is dominant, such as those in North America.
Color commentator, sometimes known a color analyst = is sports commentator who assists the play-by-play announcer by filling in any time when play is not in progress. The term is of North American origin. The color commentator provides expert analysis and background information, such as statistics, strategy and injury reports on the teams and athletes, and occasionally light humor. Color commentators are often former athletes or coaches of the sport being broadcast.
Color Under = Early high end VTRs needed follow on equipment, either externally or internally, to produce watch able color signals. The Umatic system, an early mainstay for news production was originally designed for lower end users who couldn’t afford the expensive extra equipment. So by playing a couple of tricks using the heterodyne process, it locked the color part of the signal, at the expense of a less stable black and white portion of the signal. You could play this VTR on a monitor with no additional equipment, but the “fuzziness” associated with the video was because the color was stable, but the associated black and white signal was not. VHS uses the same process.
Commissioning = The final checkout, and setup of a production trucks compliment of equipment. Occurs after equipment install into a rack ready truck.
Communications satellite (sometimes abbreviated to SATCOM) = an artificial satellite stationed in space for the purposes of telecommunications. Modern communications satellites use a variety of orbits including geostationary orbits, Molniya orbits, other elliptical orbits and low (polar and non-polar) Earth orbits. For fixed (point-to-point) services, communications satellites provide a microwave radio relay technology.
Composite video = the format of an analog television (picture only) signal before it is combined with a sound signal and modulated onto an RF carrier. Composite video is often designated by the CVBS acronym, meaning "Color, Video, Blank and Sync".
Commentator = Radio or television sports announcer narrating the event. Commentators may work from the event itself, or in some cases ‘off tube’ via the host signal while based in their home nation.
commentator information system = CIS is a real-time sport information service that provides accurate and timely data to TV viewers, radio, or online listeners and is used by sport and color commentators.
Compressor, Audio = Limits the dynamic range of audio levels to ensure audio levels do not generally exceed a certain level. Often ends up raising the average audio levels to a point where overall audio volumes sound loud to many listeners. See CALM Act.
Comps = Ususally refers to network compensation to local affiliates for airing the networks programs. This practice is slowly ending with some networks now asking their affiliates to pay the network for the right to carry their programs.
Contribution Format = Compression format with higher quality and bit rates to minimize quality loss when transporting media from a venue to the network or broadcaster. As opposed to a distribution format, which uses lower quality and bitrates to distribute the signal to the end user.
Coordinating Director = Manager in charge of other directors.
Coordinating Producer = Producer who manages the schedule for a production or event.
Copy = The written material used in producing that is meant to be read out by the announcer, talent or presenter.
Copyright = gives the author of an original work exclusive right for a certain time period in relation to that work, including its publication, distribution and adaptation, after which time the work is said to enter the public domain. Copyright applies to any expressible form of an idea or information that is substantive and discrete and fixed in a medium. Some jurisdictions also recognize "moral rights" of the creator of a work, such as the right to be credited for the work. Copyright is described under the umbrella term intellectual property along with patents and trademarks.
Countdown = A bumper which counts down to the beginning of the following broadcast. Also used for the debut of a new channel.
Crash Kit = replacement parts or circuit boards to cover for single point of failures in key production gear, such as the Production Switcher, usually carried on the truck. Sometimes found in isolated studios doing live production.
CRC = Cyclic Redundancy Check. Used for error detection in digital circuitry. A check sum is added to a block of data based on an algorithm that calculates a value base on the data payload.
Cross Conversion = Changing scan rates for synchronicity within a broadcast plant. Typically done by converting between 720p, 1080i or 1080p.
Crossfade = a technique where the A1 fades out the out going track at the same time as fading in the new track.
Cross Pole = Odd and even numbered transponders in a satellite are horizontal and vertical alternating polarities. Satellite transponders are in an arc across the sky and as such their H and V orientation changes slightly from satellite to satellite. Cross pole is where the uplink operator adjust the fine orientation of his antenna to match the satellite. This is down by rotating the satellites feed horn.
CRT = Cathode Ray Tube, the glass picture tube found in older television displays.
Cue Track = a recorded audio track containing information about upcoming events that the operating engineer should be aware of. Edison first used it on his first talking pictures using records for the sound playback. He used the information to synchronize picture and sound. On early soundtrack records the introduction of a "beep tone" was used to tell the projectionist to turn on and off the auditorium speakers so the audience would not hear the projectionist's cue information. Cue tracks were adopted in the early days of Kinescope to cue the film chain engineer and later used in early Ampex Quad Tape systems and is still used today either as voice or digitally for station automation systems. In the early days of bicycled programs cue tracks along with a printed time line was used to inform the engineer of brakes or jam (insert) spots in the tape including a 5 count to the brake in and out locations. Because the program tape or film never stopped. Often the original recording engineer would add comments of his own regarding the program, sometimes humors. When smaller networks that supported independent stations programs, were assembled and the new track often had the original engineer's voice and the assembling engineer's voice and humor too.
D
Dark Fiber = Fiber installed between two places that does not have transmitter and receive equipment connected at the ends.
DABDigital Audio Broadcasting The use of digital encoding to send higher quality or a greater number of radio services to equipped receivers.
DAC = Digital-Analog-Converter. Equipment that changes digital signals into analog
Datacasting = Is the broadcasting of data over a wide area via radio waves. It most often refers to supplemental information sent by television stations along with digital television, but may also be applied to digital signals on analog TV or radio. It generally does not apply to data which is inherent to the medium, such as PSIP data which defines virtual channels for DTV or direct broadcast satellite systems; or to things like cable modem or satellite modem, which use a completely separate channel for data.
DBS = Direct-Broadcast-Satellite. Television and radio programmes distributed by Communications satellite for reception via a satellite_dish at the receiver's property.
dB = See Decibel
dBF (Decibel Full Scale) = Used in conjunction with digital audio. dBF is the maximum level that a audio digital signal can reach, as at dBF all available audio bits are high, and thus any attempt at additional level will be clipped. dBF is an absolute and not a relative level. -24dBF, the normal targeted dialog level in digital audio means that dialog is 24 dB below the absolute possible level. 0dB is equal to dBF when referring to digital audio.
dBm = This is an absolute power measurement and not a relative one. 0 dBm equals 1 milliwatt of power into 600 ohms. It was originally established by Bell Telephone back in the 1800s. It is measured in decibels. Most electrical dB values are still referenced to this value.
Dead Air = The time on-air where there is no audible transmission. This silence can be down to any of the following:
* DJ, Producer or Engineer error
* Equipment error or failure
* Act of God
* Deliberate Silence
* Silence for remembrance
Decibel (dB) = A logarithmic non-linear scale often used in electronics and for sound. When referring to power, be it RF signals or sound levels, every 10 dB increase in value equals a ten times increase. Thus 20 dB is 10 times greater than 10, and 30 dB is 10 times greater than 20, and 100 times greater than 10dB. For voltage levels every 20 dB increase equal a 10 times increase. One tenth of a bel.
The human ear is capable of detecting an enormous range of sound intensities. Furthermore, our perception is not linear. Experiments show that when humans perceive one sound to be twice as loud as another, in fact the louder sound is about ten times as intense as the fainter one. For this reason, sound is measured on logarithmic scales. Informally, if one sound is 1 bel (10 decibels) "louder" than another, this means the louder sound is 10 times louder than the fainter one. A difference of 20 decibels corresponds to an increase of 10 x 10 or 100 times in intensity. The beginning of the scale, 0 decibels, can be set in different ways, depending on exactly which aspect of sound is being measured.
Decode = Used in a couple contexts. With compression is means the compressed data, usually video or audio, is converted back to its pre-compressed state, or as close a representation as possible. When used in an RF context it means that after the modulation scheme used to convey the data is removed the resulting data is converted back to baseband information.
Demographic data = Refers to selected population characteristics as used in government, marketing or opinion research, or the demographic profiles used in such research. Commonly used demographics include race, age, income, disabilities, mobility (in terms of travel time to work or number of vehicles available), educational attainment, home ownership, employment status, and even location. Distributions of values within a demographic variable, and across households, are both of interest, as well as trends over time. Demographics are frequently used in economic and marketing research.
De-Embedder = device which extracts embedded audio from the digital video stream.
DENG = Digital ENG. Uses digital transmission techniques.
Destination = alternate term for output of a routing switcher, or delivery of a program stream or file.
Dialnorm = This is a metadata setting that is set to indicate dialogue’s intended level. Dolby has developed circuitry and algorithms that can detect and extract dialogue from the rest of the audio. Dialnorm is usually set so dialog has a level of -24dBF. So when dialogue is present, getting dialogue levels correct for accurate delivery to the viewer is a much more reliable prospect. Dolby uses other algorithms to use other anchor elements in the audio when dialog is not present. Dialnorm is a tool used to comply with the Calm Act.
Digicart = Device manufactured by 360 systems used to playback pre-recorded audio segments. Was standard in U.S. mobile units.
Digital = system that uses discrete (discontinuous) values, usually but not always symbolized numerically (hence called "digital") to represent information for input, processing, transmission, storage, etc. Such data-carrying signals carry electronic or optical pulses, the amplitude of each of which represents a logical 1 (pulse present and/or high) or a logical 0 (pulse absent and/or low).
Digital audio uses digital signals for sound reproduction. This includes analog-to-digital conversion, digital-to-analog conversion, storage, and transmission. In effect, the system commonly referred to as digital is in fact a discrete-time, discrete-level analog of a previous electrical analog.
Digital cable is a type of cable television distribution using digital video compression.
Digital media (as opposed to analog media) usually refers to electronic media that work on digital codes. Computing is primarily based on the binary numeral system. In this case digital refers to the discrete states of "0" and "1" for representing arbitrary data. Digital media like digital audio, digital video and other digital "content" can be created, referred to and distributed via digital information processing machines. Digital media represents a profound change from previous (analog) media.
Digital networks are electronics systems that use digital signals. Digital electronics are used in computers, mobile phones, and other consumer products. In a digital circuit, a signal is represented in discrete states or logic levels. The advantages of digital techniques stem from the fact it is easier to get an electronic device to switch into one of a number of known states, than to accurately reproduce a continuous range of values, traditionally only two states, '1' and '0' are used though digital systems are not limited to this.
Digital rights management (DRM) is a generic term that refers to access control technologies that can be used by hardware manufacturers, publishers, copyright holders and individuals to try to impose limitations on the usage of digital content and devices. The term is used to describe any technology which inhibits uses (legitimate or otherwise) of digital content that were not desired or foreseen by the content provider. The term generally doesn't refer to other forms of copy protection which can be circumvented without modifying the file or device, such as serial numbers or keyfiles. It can also refer to restrictions associated with specific instances of digital works or devices.
Digital recording, the analog signal of video or sound is converted into a stream of discrete numbers, representing the changes in air pressure or chroma and luminance values through time; thus making an abstract template for the original sound or moving image.
Digital Television (DTV) = the sending and receiving of moving images and sound by discrete (digital) signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV.
Digital Terrestrial Television (DTTV or DTT) = an implementation of digital technology to provide a greater number of channels and/or better quality of picture and sound using aerial broadcasts to a conventional antenna (or aerial) instead of a satellite dish or cable connection.
Digital video = a type of video recording system that works by using a digital rather than an analog video signal.
Digital video recorder (DVR) or personal video recorder (PVR) is a device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive or other memory medium within a device.
Digitizing or digitization = is representing an object, image, sound, document or a signal (usually an analog signal) by a discrete set of its points or samples. The result is called "digital representation" or, more specifically, a "digital image", for the object, and "digital form", for the signal. Strictly speaking, digitizing means simply capturing an analog signal in digital form.
Direct Box = device to connect the output of a guitar amp or speaker into an audio system. Converts the high level signal driving a speaker to line level and provides electrical isolation via a transformer.
Direct broadcast satellite (DBS) is a term used to refer to satellite television broadcasts intended for home reception, also referred to more broadly as direct-to-home signals. The expression direct-to-home or DTH was, initially, meant to distinguish the transmissions directly intended for home viewers from cable television distribution services that sometimes carried on the same satellite.
Display resolution of a digital television or display = the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed.
Distribution Format – See Contribution Format
Diversity Receive = RF receiver that recovers RF signals from multiple paths, often arriving from different directions. Internal receiver processing uses the multiple received signals to construct a single result.
Dolby Digital, also Dolby D. = the standard for 5.1 channel (surround sound) audio. Six discrete channels are used (Left, Center, Right, Left Rear Surround, Right Rear Surround, and Subwoofer).
Doughnut = See Live Shot
Downlink(DL) = the link from a satellite to a ground station. The segment of a satellite transmission from the satellite to a receiving dish, either in a truck or at a fixed location.
Drop Box = Usually refers to a portable intercom or IFB station.
Dropping the light = Lowering the light levels. "Drop the light" is often yelled while shooting when the director wants to continue shooting the action of the scene after the light levels are lowered. It has nothing to do with any physical dropping of a lighting fixture during the scene.
DSNG - Digital Satellite news gathering = Use of digital satellite transmission from remote broadcast locations for the purpose of live television news event coverage.
DT12 = audio cable carrying 12 balanced signals with a single multipin connector on each end of the cable. There are also DT-12 Fan-out cables with individual XLR cables on one end or DT-12 Breakout Boxes with individual XLR breakouts mounted in a box.
DTH - Direct To Home = Television and radio programs distributed by satellite for reception via a dish at the receiver's property.
Dual Feed Mobile Unit = Production truck that has two production compartments; one for the home feed and a second for the away feed. Often both use the same switcher electronics with two distinct control panels. Both feeds share most other equipment in the truck, notably the routing and intercom systems, setup to segregate the two productions from each other.
Dub = Most commonly, a copy of a film or tape. It can also mean making a completely new soundtrack, as in dubbing English for a foreign film. A dubbed tape is also called a dupe.
Duce = 2,000 watt spotlight
Duct Tape = Sometimes also referred to as Duck Tape is a cloth tape sealed with polyethylene. Unlike Gaffer tape, which was designed to be cleanly removed, duct tape leaves an adhesive residue.
Dustbin Dave (UK) = The accidental deletion of all media from all video server locations within a transmission environment, resulting in a service to go to black to air (BTA).
DVB - Digital Video Broadcasting
The MPEG-2 based standard of digital transmission and reception. Comes in variants according to the type of broadcast, e.g. DVB-T for terrestrial.
DVD, also known as "Digital Versatile Disc" or "Digital Video Disc", is an optical disc storage media format. Its main uses are video and data storage. DVDs are of the same dimensions as compact discs (CDs) but store more than six times as much data.
DVD-Audio (commonly abbreviated as DVD-A) is a digital format for delivering very high-fidelity audio content on a DVD.
DVD player is a device that plays discs produced under both the DVD Video and DVD Audio technical standards, two different and incompatible standards.
DVE = Digital Video Effects. Term used to describe a device that effectively changes the size, shape and position of live video in two or three dimensions along X, Y & Z axis. Can be free standing device or built into a switcher. Called DME by Sony or DPM by Grass Valley.
DVEous = popular freestanding DVE built by Abekas.
E
E2 = the second engineer, usually maintenance on a mobile unit.
E-mem = Historically has referred to the ability of a video production switcher’s effects bank to remember a snapshot of it’s settings.
EBU = European Broadcasting Union
ECP = engineering connector panel, the places where signal cables going in and out of a mobile unit are connected. Also known as a BSP or Broadcast Service Panel. In the U.K. and Australia it is called the Tailboard.
Edison plug = standard 15 ampere rated grounded male electrical plug in the U.S. The female version is an Edison socket.
Effects Mic = Microphone used to capture the sounds of an event, like the crack of a baseball bat, the “bang” of a basketball off the backstop, the audible of a quarterback, the sounds of skates on ice, etc.
EFP = Electronic Field Production. Usually refers to commercial or program production where a television camera is used in film style shot.
EIC = Engineer in Charge. The person who is responsible for proper technical operation of the truck. Usually works for the vendor who owns the truck. The EIC has the delicate job of looking after the welfare of the unit while looking after the needs of the client at the same time.
Embedded Audio = audio which has been inserted into the digital video signal stream, allowing audio and video to be transported in perfect synchronization over one circuit.
Embedder = device which inserts audio into the video streams, usually up to eight stereo pairs, or 16 channels.
Encoder = In the context of compression an encoder takes baseband video or audio and compresses it to limit the bitrate or bandwidth required. With RF if takes baseband audio, video, or data and organizes it to be modulated onto an RF carrier.
Encryption = The scrambling of a signal to allow reception via a decoder only be specific viewers, e.g. after the payment of a fee.
ENG = Electronic News Gathering = using a portable lightweight field camera. Typically used by a small production (or ENG) crew.
ENG Truck = Usually a van with rudimentary production capability and a microwave transmitter to get signals back to the studio.
EPG (Electronic Program Guide) = Channel and program listing service available on digital TV.
EPG Ethernet = a family of frame-based computer networking technologies for local area networks (LANs). The name comes from the physical concept of the ether. It defines a number of wiring and signaling standards for the Physical Layer of the OSI networking model, through means of network access at the Media Access Control (MAC) /Data Link Layer, and a common addressing format.
ERP = Effective Radiated Power (of a transmitter)
Establishing shot sets up, or "establishes", a scene's setting and/or its participants. Typically it is a shot at the beginning (or, occasionally, end) of a scene indicating where, and sometimes when, the remainder of the scene takes place.
EVS = Manufacturer’s name for an industry standard video disk recorder used for slow motion replays and creating highlights packages.
Executive Producer = Producers report to this person. Often the Executive Producer is the head of the sports or news departments of the network or station.
External Key = See Key - Video
F
F#&@ the Truck = expression taught to new utilities and remote newbies- always run the male end of the cable to the truck. The first time you run a one thousand foot cable the wrong way, you remember. Doing it in the rain promotes greater retention of the concept as well.
Fader = An audio pot or attenuator at a mixer.
Fax = Facilities Check. Before the show the production staff in concert with the technical staff and most other crew members check that all sources are available where needed, all feeds make it to their destination, that all camera tallies light when required, and that talent have working IFBs
FCC - Federal Communications Commission = The regulator of broadcasting in the United States.
fec - forward error correction. Additional data added to the payload that can be used to re-construct data that is lost in transit.
Feed = television or radio program transmitted, or fed, to Broadcast Partners.
Feedback = a loud noise produced when the amplified sound from an output ( loudspeaker ) is picked up by an input ( microphone, phonograph ) feeding that loudspeaker. This can be potentially damaging to both the speaker(s) in question, as well as the hearing of the subjected listener. This may also occur when an input is directly patched into an output of the same device, usually due to operator error.
In radio broadcasting, feedback may occur when a DJ increases his or her headphone volume to a high enough level that the microphone is able to pick up the sound coming from the headphones, usually when the DJ's head is turned to one side.
Fiber – Single and Multi-Mode = Single-mode fiber cable is usually used instead of multi-mode. For long paths, single-mode is required. Multi-mode cable has thicker fiber strands than single-mode, and thus the laser light signal will reflect, or bounce from the outside fiber perimeter to the opposite outside perimeter as it travels down the cable. This causes light transmitted down the fiber, to have varying transit times end-to-end, causing ambiguity between successive data bits, especially as the path gets longer. Single mode has thin enough fiber strands that the light doesn’t reflect from side to side down the fiber strand.
File Wrapper = See Wrapper
Final Cut = Final Cut Pro, popular editing software from Apple, powerful yet inexpensive.
Flash Van = A “flash” van is an industry term for a vehicle at the Olympics that moves from venue to venue as needed, adding temporary additional capability to a venue, usually in the form of graphics and replays.
Flash interview = brief interviews of racers done just before or immediately after the race. Often used as a term to describe an interview as part of the multilateral world feed.
Floodlights are broad-beamed, high-intensity artificial lights often used to illuminate outdoor playing fields while an outdoor sports event is being held during low-light conditions.
Flown = General refers to cables are extended off the grown from one location to another. Anytime cables have to be off the ground they are referred to as “being flown”.
Fly Case Production- or Fly Pack = a portable live video production systems with multi-cam monitoring, switching and communications. All components are shock-mounted in airline checkable heavy-duty cases.
Fostek = small self-powered speaker in rugged case built by Fostek Electrronics. Now almost a generic term for this type of device.
Fox and Hound = A test set used to check and identify particular cables. The fox half of the unit puts a tone on a cable while the hound half is used to sniff for the other end of the cable. Via inductance the hound doesn’t actually have to touch the wire’s conductor, just be brought close to it. These two pieces are also known as toners and sniffers.
Fox Box = The graphics put up over a game. Usually has pertinent current stats above the status of a game. While originally a rectangle or square box, pioneered by Fox, today it is often a ribbon along the top of the screen.
FPS - Frames per second = The number of times the television is refreshed in a second of time. As a rule of thumb, this is the same as the local Alternating Current electricity supply - 60 Hz or 50 Hz. Originally when television was first devised in the 1930s electronic circuitry was not stable enough to base frame rates on frequencies not equal to the local power frequency.
Frame Rate Conversion (FRC) = A technology to synchronize and change frame rates between two formats (ie: film to video, PAL to NTSC, 50 Hz. to 60Hz. etc..)
Frame Sync = Short for frame synchronizer. This device takes an incoming video signal that is not locked to local video and locks it to local reference so that the video can be used in effects combinations with other local sources. Up until the mid-80s instead of locking an external incoming signal to local reference, the opposite was done as local sources would all be locked to the external signal in a process called Genlocking.
Fronthaul = a broadcast video feed that is complete with graphics, commercials, interstitials and studio integration. This typically originates from a Master Control Room and is delivered to a distributor or over-the-air (also see backhaul)
Frame rate, or Frame frequency, is the measurement of the frequency (rate) at which an imaging device produces unique consecutive images called frames. The term applies equally well to computer graphics, video cameras, film cameras, and motion capture systems. Frame rate is most often expressed in frames per second (FPS) and in progressive-scan monitors as hertz (Hz).
Free-To-Air Channels = No subscription fee is payable in order to view the channel. The majority of the channels on the digital terrestrial platform are free-to-air channels.
Frequency = The number of cycles per second of wave signal. Measured in Hertz (Hz) or kilohertz (kHz) or MegaHertz (mHz).
G
Gaffers Tape = See Duct Tape
Gain = Volume
Gamma = Camera imagers tend to emphasize whites or brighter luminance values, and under amplify blacks or low lights. The term gamma originally simply stood for the transfer function (output versus input) and was one of the Greek characters used to describe various parameters. To compensate for the non-linearity of levels, an opposite emphasis – the stretching of blacks and compression of whites - was added to processing circuitry that followed the imager.
Gender Bender = An adapter used to change the sex of a connector, either from pins to sockets or visa-versa.
Genelec = standard brand of monitor speaker used in U.S. mobile units in the first decade of the 21st century.
Genlock (for Generator Lock) = a common technique where the video output of one source, or a specific reference signal, is used to synchronize other television picture sources together. The aim in video and digital audio applications is to ensure the coincidence of signals in time at a combining or mixing or switching point. When sources are synchronized in this way, they are said to be genlocked.
Gig = A job at an event
GHz – Gigahertz = Thousand million cycles per second. The measurement for satellite frequencies.
Glass Cockpit = Term burrowed from airplane cockpits where many individual displays and controls are incorporated into a few large displays. Applied to monitor walls in trucks and other facilities today that replaced many individual CRT displays with fewer larger displays.
Goodnight = The process of letting the backhaul provider know that the venue is done with using the path as the show or production has ended. Often done with a graphic put up with a simple “goodnight”, usually this also involves a phone call.
Greenie = A small screw driver with a green handle originally sold by Xcelite. Over the last 20 years equipment that had “potentiometers” (variable resistors) of various quantities, which were there for adjusting analog values have mostly disappeared. With digital technology today this tool is becoming less needed.
Grips = See Utilities.
Ground Loop = Unintentional current flow through a truck. Often manifests itself hum in analog audio.
GOP (Group of Pictures) = In compression this is the number of successive video frame from one anchor frame to the next.
GPS = Global Positioning Satellite
GMT Greenwich Mean Time, which is constant and often used to determine event schedules and running orders, given that the value of GMT is a common medium and not affected by regional daylight saving adjustments.
H
H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC (Advanced Video Coding) = a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video. H.264 is perhaps best known as being one of the codec standards for Blu-ray Discs; all Blu-ray Disc players must be able to decode H.264. It is also widely used by streaming internet sources, such as videos from Vimeo, YouTube, and the iTunes Store, web software such as the Adobe Flash Player and Microsoft Silverlight, and also various HDTV broadcasts over terrestrial (ATSC, SBTVD, DVB-T or DVB-T2), cable (DVB-C) and satellite (DVB-S and DVB-S2).
Hairpin = A jackfield patch that connects the top of a jackfield to the bottom. While most patch panels today are setup to normally complete that path internally these are still often used to signify that the path is indeed being used and that it is not to be interrupted.
Handheld Camera = a camera that is shoulder mounted or carried about by the camera operator.
Hard Camera = either a studio camera or a handheld camera configured to have the attributes of a studio camera.
Hard Disk Recorder = a type of recording system that uses a high-capacity hard disk to record digital audio or digital video. Hard disk recording systems represent an alternative to more traditional reel-to-reel tape or cassette multitrack systems, and provide editing capabilities unavailable to tape recorders. The systems, which can be standalone or computer-based, typically include provisions for digital mixing and processing of the audio signal.
HB - Host Broadcaster. = A production company or local television network providing the basic television broadcast from a specific event, intended for integration with commentary teams from different rights holding nations, or for local integration with attending RHB.
HD - HDTV - High-definition television = Broadcasting using a line standard of 720 or greater. Prior to World War II, high definition meant a line standard greater than 240 lines. Any video system of higher resolution than standard-definition (SD) video, and most commonly involves display resolutions of 1280×720 pixels (720p) or 1920×1080 pixels (1080i/1080p).
HDMI - High-Definition Multimedia Interface = standard for interconnecting devices such as monitors, DVD players, Blu-Ray Players.
HDV = a format for recording and playback of high-definition video on a DV cassette tape.
Head Clog = Rapidly becoming an archaic term – when a VTR head’s gap would become clogged with tape oxide and would either quit recording or playing back.
Hertz (symbol: Hz) = a unit of frequency. It is defined as the number of cycles per second. It is the basic unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), and is used worldwide in both general-purpose and scientific contexts. Hertz can be used to measure any periodic event; the most common uses for hertz are to describe radio and audio frequencies, more or less sinusoidal contexts in which case a frequency of 1 Hz is equal to one cycle per second.
Heterodyne = The process of mixing two separate frequencies together to generate another frequency. Used to shift a RF signal on one frequency to another. Used for 100 years for AM and FM receivers, and later television receivers. Still used in many satellites for converting uplink frequencies into the proper downlink frequencies.
Hi5 = device from AJA to convert HD-SDI signals to HDMI. Allows consumer flat panel displays to be connected to HD video feeds on coax.
Host Feed = Generic feed from the IBOC that has nothing specific to any country. Broadcasters carrying the Olympics take this feed and add additional cameras, announcers, and graphics of there own to produce their own coverage. The host feed is generated by the IBOC. The host feed is also known as the multilateral feed, while individually produced broadcaster feeds, such as NBC’s or the Bell/Rogers consortium in Canada (CBC for the 2014 Olympics) or Televisa in Mexico are known as unilateral feeds.
Hum Bucker = deviced used to eliminate hum induced into video signals by A/C power ground loops. The hum appears as rolling black bars in the picture, Hum Buckers eliminate it.
I
I/O = input and output connections
IEC = International Electrotechnical Commission
Ident = A station's symbol or logo, often accompanied by music, a jingle or an animation.
IDTV = Integrated Digital television
IFB = Interrupted Feed Back or Interrupted Fold Back. Talent generally has program audio sent to an earpiece. The IFB system has to ability to interrupt that program feed so that the director, producer, or other can relay instructions or information to the talent.
International Broadcast and Operations Center (IBOC), also IBC = Facility at the Olympics operated by the Olympic Committee to host broadcasters from around the world and which produces the Host Feed.
Instant replay = a technology that allows broadcast of a previously occurring event using recorded video. This is most commonly used in sports; by on television to replay previous plays for the viewer, often from other angles than shown in the main broadcast, and also on video screens at live events. The viewer and commentators often watch the footage at a slow motion frame rate to allow more detailed analysis. More advanced technology has allowed for more complex replays, such as pausing, and viewing the replay frame by frame.
Interactive television (generally known as iTV) = describes a number of techniques that allow viewers to interact with television content as they view it.
Intercom = a stand-alone electronic communications system intended for limited or private dialogue. Intercoms can be portable but are generally mounted permanently. Intercoms can incorporate connections to walkie talkies, telephones, cell phones and to other intercom systems over phone or data lines and switch electronic or electro-mechanical devices such as signal lights and door latches.
Interlaced = scanning scheme where rows of pixels are captured and displayed as alternate fields. Field 1 has all odd number lines, field two as even number lines, effectively reducing the bandwidth required in half. Your eyes see the images of each field as one frame. Biological de-interlacers.
Internal Key = See Key - Video
Internet = a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standardized Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP). It is a network of networks that consists of millions of private and public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope that are linked by copper wires, fiber-optic cables, wireless connections, and other technologies.
IPTV = Internet Protocol Television = method of delivering television services via broadband.
IRD = Integrated Receiver Decoder
ISDN = Integrated Switched Digital Network = a telephone-like digital technology which permits better audio quality for transmission and a number of implementation types allowing digital data transfer.
ISO = International Organization for Standardization or Isolated Camera
Iso Transformer – Isolation Transformer = device used to provide electrical isolation in an audio path, general to reduce hum in the audio. Most professional audio consoles have transformer-isolated inputs.
Isolated Camera = A camera that is generally covering one aspect or a particular player in an event.
ITU - International Telecommunication Union = Originally the International Telegraph Union, the ITU is the international organization established in 1865 to standardize and regulate international radio and telecommunications.
ITV - interactive television = Systems that allow viewers to interact (e.g. play games, shop for related items or find further information) either two-way, via a telephone line, or one-way, via MHEG graphics.
ITV - Independent Television = The UK's first commercial television network.
J
Jib (camera) = a boom device with a camera on one end, and a counterweight and camera controls on the other. It operates like a see-saw, but with the balance point located close to the counterweight, so that the camera end of the arm can move through an extended arc. A jib permits the camera to be moved vertically, horizontally, or a combination of the two. A jib is often mounted on a tripod or similar support.
Jingle = A produced programing element usually in the form of vocals to accompanying music often produced in-house to identify the show, DJ or the station.
Joystick = slang for camera remote control panel. Officially called an RCP (Remote Control Panel ) or OCP (Operators Control Panel.)
K
Key Video = When video in a scene is replaced with the video of another source. An internal key uses nothing but video levels to determine what part of the video is replaced by another. The signal to be keyed is inserted over the original video whenever its video level reached a preset level. An external key uses an external whole cut signal to determine where video is replaced. This produces much better results than an internal key but requires a separate whole cut video signal. Most graphic devices provide this signal. A linear key is an external key where the video is not keyed via a “go/no go” signal level but combines a video mix with the key so that the keyed video can have varying degrees of opaqueness. A chroma key is a key not only based on video level, but primarily based on color in the video to be keyed over.
Key Frame = Effects in a DVE/DME and switcher are often based on key frames, essentially a milestone in the effect. A key frame will start the effect and the next key frame will be designate how the effect will look at that instant. A series of successive key frames will serve as snapshots as to how an effect progresses from start to stop. These key frames are created along a timeline that indicates how much time elapses from one key frame to the next.
kHz – Kilohertz = Thousand cycles per second. kHz is used to measure mediumwave and often shortwave frequencies.
KP = intercom station or key panel. Usually followed by a number which indicates the number of keys, such as KP32.
Ku band (pronounced "kay-yoo") = a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in the microwave range of frequencies. This symbol refers to "K-under" (in the original German, "Kurz-unten", with the same meaning)—in other words, the band directly below the K-band. In radar applications, it ranges from 12 to 18 GHz according to the formal definition of radar frequency band nomenclature in IEEE Standard 521-2002. Ku band is primarily used for satellite communications.
L
Land Line = dedicated ground based / terrestrial circuit.
Latency = Usually used in context of audio, video, and RF signals. Latency is the time it takes a signal to travel over a path or through a piece of equipment.
LCD = Liquid Crystal Display
Lead Tape Operator = plans and supervises the recording, playback and replay operation on a remote.
Legal ID = In the US, the station identification consisting of the station call letters followed by the community of license. Given as close as practical to the top of the hour at a natural break in program offerings.
Letterbox = The appearance of black bars at the top and bottom of a picture when 16:9 or 14:9 widescreen material is shown on 4:3 sets. See also pillar box and postage stamp.
Limiter – Audio = Device that hard limits, or chops, audio levels above a certain level, as opposed to a Compressor for audio.
Line standard = The number of lines broadcast to make up a television picture. Generally, in SD - 525 in NTSC areas and 625 elsewhere.
Linear = Anything that progresses in a fixed manner. A signal is linear if the signal into a device has a constant relationship to the output. The slope the signal follows out might be different but it is straight and not bent upward or downward. See Gamma. Linear also corresponds to editing. See Linear video editing.
Linear Key = See Key – Video
Linear video editing = the process of selecting, arranging and modifying the images and sound recorded on videotape whether captured by a video camera, generated from a computer graphics program or recorded in a studio. Until the advent of computer-based non-linear editing in the early 1990s "linear video editing" was simply called "video editing."
Live = Any programming which is broadcast immediately as it is being delivered (a live report); performed (a live concert or show); or captured (live news or sports coverage). Requires an unbroken communications chain without any intervening recording or storage technology. Considered the most exciting form of broadcasting, delivered "as it happens."
Live on tape = A recorded program produced in real time, usually with a studio audience, for later broadcast. Requires precisely timed pauses for insertion of station breaks and commercials at time of broadcast. Typically employed for network broadcast across multiple time zones. Also applies to live broadcasting which is simultaneously recorded for rebroadcast at a later time or date.
Light = electromagnetic radiation, particularly radiation of a wavelength that is visible to the human eye (about 400–700 nm, or perhaps 380–750 nm). In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not.
Liquid Crystal Display LCD = the technology used for displays in notebook and other electronics devices. LCDs allow displays to be much thinner than cathode ray tube (CRT) technology. LCDs consume much less power than LED and gas-display displays because they work on the principle of blocking light rather than emitting it.
Live Shot = Usually applies to ENG/SNG, where a microwave or satellite news truck will send video and audio live back to the station for immediate air. Often involves a stand-up with a pre-edited package, either done on site or back at the station, in the middle of the live shot. Sometimes referred to as a doughnut.
Live television or Live refers to television broadcast in real time or on a short tape delay basis. It is used in the local news.
Live to tape = to pre recorded program produced in real time, usually with a live audience, for later broadcast. Requires precisely timed pauses for insertion of station breaks and commercials at time of broadcast. Typically employed for network broadcast across multiple time zones. Also applies to live broadcasting which is simultaneously recorded for rebroadcast at a later time or date.
Local area network (LAN) = a computer network covering a small physical area, like a home, office, or small group of buildings, such as a school, or an airport. The defining characteristics of LANs, in contrast to wide-area networks (WANs), include their usually higher data-transfer rates, smaller geographic place, and lack of a need for leased telecommunication lines.
Long shot (sometimes referred to as a full shot or a wide shot) typically shows the entire object or human figure and is usually intended to place it in some relation to its surroundings. It has been suggested that long-shot ranges usually correspond to approximately what would be the distance between the front row of the audience and the stage in live theatre. It is now common to refer to a long shot as a "wide shot" because it often requires the use of a wide-angle lens. When a long shot is used to set up a location and its participants in film and video, it is called an establishing shot.
LNB = Low Noise Block-downconverter (with amplifier). Its purpose is to convert a block of high frequencies (microwave) to a block of lower frequencies which can be passed down a coaxial cable.
Loom = multiple coax cables married together under a common outer jacket.
Lower third = Portion of screen of regular broadcast reserved for textual and static visual content; i.e., news ticker, time, title of segment, title of programme, channel bug, etc. Upper third has sometimes been used alongside lower third, as in the case of MSNBC since 2010.
M
Ma Bell = Slang term for the old AT&T long lines and the baby bells that were broken up in the 1980s. Still used to refer to a local phone company.
Macrovision = A trademarked system designed to prevent unauthorised copying of video material.
MADI = Multichannel Audio Digital Interface = a standard for the transport of multiple audio channels. It supports serial digital transmission over coaxial cable or fibre-optic lines of 28, 56, or 64 channels; and sampling rates of up to 96 kHz with resolution of up to 24 bits per channel. Originally developed for recording studios to connect multi-track recorders to and from consoles. For remote use it often ties consoles to routers and moves audio between trucks at the console or router level.
Married Pair = two audio cables bonded or taped together, used to connect the talents microphone and IFB to a breakout box. Often has one black and one brown cable with one male and one female connector on each end. Properly made, the talent end microphone cable is about three feet longer than the IFB cable to allow for hand held mic and IFB belt-pack.
Mastering = The process of taking the final audio and transferring, sometimes with additional processing, onto the final storage medium.
Media = in television generally refers the device or material video, audio, and graphics are recorded on, such as film, videotape, or disc-drive.
Media clip = a short segment of media, either an audio clip or a video clip.
Media server = either to a dedicated computer appliance or to a specialized application software, ranging from an enterprise class machine providing video on demand, to, more commonly, a small personal computer or NAS (Network Attached Storage) for the home, dedicated for storing various digital media (meaning digital videos/movies, audio/music, and picture files).
Meld = Playback highlights packet that is continually updated, or built as an event unfolds.
Metadata = Data about data, in television that usually means data about media. Can be part of a file or transport stream or travel independently of the file/stream that the media is in.
MHz = Million cycles per second. The bandwidth area for FM broadcasts and television.
Mic Flag = Block that mic is inserted into below its pickup capsule or grill and below where the report grips the mic that shows the owner of the mic.
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from 1mm - 1m, or frequencies between 0.3 GHz and 300 GHz.
Mix -Minus = An audio feed where all the audio elements are present except the speakers own voice. This is necessary when the latency from a remote venue to where the audio is mixed, and then back again to the venue is such that the speaker will hear themselves delayed enough to cause distraction. Mix-minus, when used is fed to the speaker’s IFB feed. Often when you see a reporter pull their IFB earpiece out during a stand-up it means that they are not receiving mix-minus and are also hearing themselves.
Mnemonics = The shorthand that equipment and positions on a truck will be called as many pieces of equipment, such as routers and intercoms can only handle certain length names. Thus Camera 1 will usually be given a name such as Cam 1, and the director a name such as Dir.
Mobile Uplink or SNG = a mobile communications unit for the purpose of remote broadcasting. Mobile units are usually vans equipped with advanced, two-way audio and video transmitters and receivers, using dish antennas that can be aimed at geostationary satellites.
Mobile Unit (M/U) = Mobile production television control room used to produce remote coverage of an event, using a range of standard broadcast facilities.
Money Reel = Originally a reel of tape that contained commercial spots to be played from the truck, now a server or other media device.
Mono = Single channel audio
Mouse hole = Most truck compartments will have one or more small access ports, or wickets, known in the in the vernacular as a "mouse holes" to allow cables to be run into the truck when no normal IO path exists for them. Often, new and unexpected equipment is cabled to the outside world via mouse holes.
MPEG = The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) was formed by the ISO to set standards for audio and video compression and transmission.
MPEG4 = a patented collection of methods defining compression of audio and visual (AV) digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) under the formal standard ISO/IEC 14496. Uses of MPEG-4 include compression of AV data for web (streaming media) and CD distribution, voice (telephone, videophone) and broadcast television applications. MPEG-4 absorbs many of the features of MPEG1 and MPEG2 and other related standards, adding new features such as (extended) VRML support for 3D rendering, object-oriented composite files (including audio, video and VRML objects), support for externally-specified Digital Rights Management and various types of interactivity. AAC (Advanced Audio Codec) was standardized as an adjunct to MPEG2 (as Part 7) before MPEG4 was issued.
msb = most significant bit
MTBF = Mean Time Between Failures
MSTS = Multi-Service Transport Stream
Muffs – Single or double = Earpieces that cover the ears on a headset, muff referring to the ear coverings on “ear muffs”. Single means only one ear is covered, two meaning both are covered. In loud situations and venues often talent and crew will wear double muff headsets.
Multi-mode optical fiber (multimode fiber or MM fiber or fibre) = a type of optical fiber mostly used for communication over shorter distances, such as within a building or on a campus. Typical multimode links have data rates of 10 Mbit/s to 10 Gbit/s over link lengths of up to 600 meters—more than sufficient for the majority of premises applications.
Multilateral = The term used to describe the international world feed, broadcast signal or running order, where the distribution of a signal or service is designed for the international market.
Multipath = When a RF signal takes many paths to a receiver. This happens often in downtown settings where the signal can bounce of many building and obstacles before it is received at the receiver. With old analog television signals this was a common cause of “ghosting”. Today microwave and wireless microphones commonly face multipath issues. Diversity Receivers are deployed to mitigate this.
Multiplexing (also known as muxing) = a process where multiple analog message signals or digital data streams are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share an expensive resource. For example, in telecommunications, several phone calls may be transferred using one wire. It originated in telegraphy, and is now widely applied in communications.
Multiplex = a bundle of digital channels broadcast as a single entity
Mults = A large cable that is made up of many smaller internal cables. Often used to carry multiple audio feeds. In many instances fiber optic cables are replacing these cables.
MUX = Multiplex
N
NAB = National Association of Broadcasters The U.S. broadcasters trade association.
NAS (Network Attached Storage) = Storage that is available to clients/PCs over the network.
Nat/VO - Video only with natural sound = Video with natural sound played at full volume intended to accompanied by a news correspondent reading a news story.
Natural Sound = Audio of only the background sounds of an event, no announcers. Also known as NAT Sound for short.
NBC (National Broadcasting Company) = A television network in the United States. Formerly also a radio network.
Network = A system which distributes programming to multiple stations simultaneously, or slightly delayed, for the purpose of extending total broadcast coverage beyond the limits of a single radio or television signal.
NEMO = (Not Emanating Main Office) An early term used in remote broadcast operations. It was often used to refer to the remote lines that fed live programming from dance halls, ballrooms, clubs and sporting events to the station's master control.
Net Return = return signal from the Broadcast Center. Can be off the air, from cable or a dedicated return path via land line or satellite. Often shows what is actually being transmitted from the Broadcast Center to the home viewer. I a dedicated path, it can be switched to allow content to be sent to the Mobile Unit from the Broadcast Center.
NDA = Non-Disclosure Agreement
NOC = Network Operations Center. The facility, usually at a network or program supplier’s main technical facility that the backhaul is sent to.
Nonl-inear editing (NLE) for film and television postproduction = a modern editing method which involves being able to access any frame in a video clip with the same ease as any other. This method is similar in concept to the "cut and paste" technique used in film editing. Non-linear, methods began to appear with the introduction of digital video technology.
NTSC (National Television System Committee) = An American committee formed to set the line standard and later color standard for broadcasting. Gave its name to the method of color reproduction used in the Americas (except Brazil) and in Japan.
O
OB Van/ Truck Outside Broadcast Vehicle = Sometimes additional vehicles are used as dedicated videotape or graphics support vehicles, and are designed to integrate with the principal OB vehicle. See Remote Truck and Mobile Unit.
Offline editing = the film and television post-production process in which raw footage is copied and edited, without affecting the camera original film or tape. Once a program has been completed in offline, the original media will be conformed, or on-lined, in the online editing stage.
One Ton of Cooling = One ton of cooling is what a ton of ice would provide, a measure from the 19th century still in use. In BTU terms, 12,000 BTU/hr or heat also requires one ton of cooling.
Online editing = generally the final stage of video editing. When the offline edit is complete, the pictures are re-assembled at full or 'online' resolution. An edit decision list or equivalent is used to carry over the cuts and dissolves from the offline.
Optical (UK) and film = Generically, any on-screen graphic. Specifically, a graphic inserted between a program and an advertisement or between individual advertisements.
Optical fiber cable = a cable containing one or more optical fibers. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable will be deployed.
Optical fiber connector terminates the end of an optical fiber, and enables quicker connection and disconnection than splicing. The connectors mechanically couple and align the cores of fibers so that light can pass. Most optical fiber connectors are spring-loaded: The fiber endfaces of the two connectors are pressed together, resulting in a direct glass to glass or plastic to plastic contact, avoiding any glass to air or plastic to air interfaces, which would result in higher connector losses.
OSHA Cord = west cost term for a power cord with Edison plug on one end, IEC power connector on the other.
Over-the-air = local television station’s transmission of its signal through the air.
P
Public Address (PA) = The audio feed for the spectators at a venue. Often for a sports event it isn’t much more than an announcer. For entertainment shows it often includes all audio elements of the show, from bands, to announcers to other talent. Often the television production truck will either produce the entire PA feed, or provide some input into the PA mix, or even be a recipient of the PA feed.
Package = A program element that can run from a couple minutes to much longer that is a completely edited and produced piece of media. While it might have an intro from a live announcer once started it generally runs until completion without any other live interruption.
Painting (camera) = When the video operator manually adjusts the color look of a camera to make it have a warmer look (more red), or a cooler look (more blue), or with today’s technology to change the color of a single color in the shot, as to make an apple more red.
PAL - Phase Alternating Line = Television broadcast system used in Europe and Australia & New Zealand, also parts of Asia, Africa and South America.
Packetization = Media and other data that is broken up into short groups and inserted into transport streams.
Panning refers to the horizontal movement or rotation of a still or video camera, or the scanning of a subject horizontally on video or a display device. Panning a camera results in a motion similar to that of someone shaking their head "no".
Parabolic microphone = a microphone that uses a parabolic reflector to collect and focus sound waves onto a receiver, in much the same way that a parabolic antenna (e.g., satellite dish) does with radio waves.
Party Line = Intercom where a group of people are all on a common intercom circuit. All conversation is heard by all. Early intercoms where all partly lines. PL, for party line, was often used to refer to the intercom, although some claim it stood for Phone Line, as very early on intercom was sometimes referred to a "phones."
Passive = Means that no electronics is involved. Usually means doing something with wiring alone.
Pay-per-view (often abbreviated PPV) offers a system by which a television audience can purchase events to view on TV-monitors via private telecast of that event to their homes. The broadcaster shows the event at the same time to everyone ordering it, as opposed to video on demand systems, which allow viewers to see the event at any time.
PCR = (UK) Program Clock Reference or Production Control Room (US)
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or work loads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application. They are said to form a peer-to-peer network of nodes.
PFL = Pre-fade Listen. Facility on a mixing desk that allows the operator to listen to a piece of audio and set levels before putting the audio to air. Also referred to as "cue."
Phono = A type of connection used for audio (RCA).
PID = Packet Identifier
Pigtail = A group of cables that converge into one large connector at one end and at the other ends each cable has its own separate connector.
Pillarbox = The appearance of blank bars on either side of the picture when 4:3 material is shown on a 16:9 widescreen television set.
Pilot = A one-off episode of a proposed series, usually in extended form, to gauge audience reaction. If successful, the rest of the series is made and the pilot becomes the first episode.
Pink Noise = Test signal that has energy across a wide spectrum that has it’s power density fall off at 10 dB per octave, as opposed to white noise with has noise energy that is flat across the spectrum. Pink noise is useful for adjusting audio equalization.
Pixel = The smallest distinguishable and resolvable area in a video image. A single point on the screen. In digital video, a single sample of the picture. Derived from the words picture element.
PL = See Party Line
Platform = A term encompassing the various ways in which a home can receive television. The six platforms are: analogue terrestrial; analogue satellite; analogue cable; digital terrestrial; digital satellite; digital cable.
Playout = a term for the transmission of radio or TV channels from the broadcaster into the networks that delivers them to the audience. Those networks can consist of terrestrial transmitters for analogue or digital radio and TV, cable networks or satellites (either for direct reception, DTH, or intended for cable headends).
Point-of-Presence (POP) = A facility or location that has direct connection to long-haul transmission paths. Usually fiber and based on Telco technology.
Point-of-view camera = Camera that is usually locked and place with no attendant operator.
POP = See Point-of-Presence
Portable multimedia player (PMP) = Sometimes referred to as a MP3 player, a consumer electronics device that is capable of storing and playing digital media. Digital audio players (DAP) that can also display images and play videos are PMPs. Like DAPs, the data is typically stored on a hard drive, microdrive, or flash memory.
Posse = A mini-fleet of trucks, possible six or more trailers that travel as one large unit. These are usually found covering NASCAR races.
Post-production occurs in the making of motion pictures, television programs, radio programs, videos, audio recordings, photography and digital art. It is the general term for all stages of production occurring after the actual end of shooting and/or recording the completed work.
Postage stamp = The appearance of a black border all around the picture, usually in error, when 4:3 material is converted to 16:9 and then back to 4:3 before broadcast.
Pot (Potentiometer) = A round knob control for increasing or decreasing the volume on a channel. Also used as a verb, as in "pot up" (increase volume, typically but not always from nothing) or "pot down" (lower volume, sometimes to nothing).
POV = See Point-of-view camera
PPM = Peak Program Meter. Meters on a mixing desk that monitor audio levels
Pre-Production = Program production, the building of packages, graphics, and effects, along with video recording of raw footage used to build packages, all done before the actual event production.
Pro-Channel = Audio channel carried on a broadcaster’s main transmission signal that allows the station to talk to news crews in the field.
Producer = The person who performs or manages the day to day business operations of a station. Also the person responsible for an individual program - a radio producer or a television producer.
Professional video camera (often called a television camera even though the use has spread) = a high-end device for recording electronic moving images (as opposed to a movie camera, that records the images on film). Originally developed for use in television studios, they are now commonly used for corporate and educational videos, music videos, and direct-to-video movies.
Production Book = Series of documents that contains technical and logistical details concerning a particular remote production.
Progressive = scanning system where row of pixels (lines) are captured and displayed one after another.
Promo = An announcement (either recorded or live) used to promote the station's image or other event.
Proxy = A low-resolution copy of hi-resolution media so that it can be viewed over low-bandwidth paths, such as by internet browser.
psf = Progressive Segmented Frame, a scheme created by Sony to transport progressively scanned 24 frames per second over infrastructure designed for 1080i/29.97
PSA (Public Service Announcement) = A PSA is intended to change the public interest, by raising awareness of an issue, affecting public attitudes, and potentially stimulating action.
PPV = Pay Per
PVR - Personal Video Recorder
Q
QAM = Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
QOS = Quality Of Service
QPSK = Quaternary Phase Shift Keying
Quadraphonic = Sound reproduction utilizing four speakers. Now superseded by Dolby 5.1 Surround Sound.
R
Rack Unit = A unit of measure used in racks that designate how tall a piece of equipment is when installed in a rack. One rack unit or RU is 1.75 inches tall (44.45 mm). A typical height of a rack in RU is 42. A piece of equipment that is said to be 4 rack units tall has a height of 7 inches.
Rack Ready = A production truck or trailer with all racks, consoles, power, environment, carpeting and other trim installed and is now ready for the actual equipment to be installed. This is one of the last steps of building a truck. Commissioning and shakedown are all that is left.
Racks = Control panel where several television cameras are matched together by operator(s) for exposure, color balance and black level. A cabinet housing equipment, usually 19” wide opening.
Raw footage = Media received that has not been edited yet.
Raw image format = A camera raw image file RAW contains minimally processed data from the image sensor of either a digital camera, image or motion picture film scanner. Raw files are so named because they are not yet processed and therefore are not ready to be printed or edited with a bitmap graphics editor. Normally, the image is processed by a raw converter in a wide-gamut internal colorspace where precise adjustments can be made before conversion to a "positive" file format such as TIFF or JPEG for storage, printing, or further manipulation, which often encodes the image in a device-dependent colorspace.
Rattler = now a generic term for compact electric/optical converter allowing coax/BNC signals to be transported over fiber.
RCA = A type of connection used for audio (Phono).
Redlines = Design drawings marked up with changes.
Remote = In terms of television production a remote is any production that is done outside a facilities main production studio. A broadcast coming from outside the studio.
Remote Pickup = A televised remote production.
Remote Truck = A vehicle, be it a van, a box/cab truck, or tractor/trailer that does remotes.
RF = Radio Frequency. Often used to refer to connections carrying TV signals in the UHF band.
RFMOD (RF modulator) = A unit which superimposes video and audio signals onto a Radio Frequency carrier signal.
RGB = The three primary colour signals: red, green, and blue (RGB) that together convey all necessary picture information. In normal high definition digital video, these three primary components are scaled such that the extreme values are code words 040h (64) and 3ACh (940) in a 10-bit representation.
RHB Rights Holding Broadcaster(s). RHB may attend selected events to allow them to customise their programming by a method of integration with the host feed. RHB also may remain in their home nations and produce television shows based on studio presentation and commentary integrated with the incoming host
Riggers = Crew members that often work at heights building scaffolds, camera platforms and installing lighting grids, and doing other activities that require climbing.
RJ = prefix for common cable, suffix indicates usage. RJ-45 for Ethernet, RJ-11 for telephones and RJ-12 is used on RTS KP panels.
Routing Switcher = simply defined as a device that can connect audio, video or data sources to destinations. Selections are generally made on Router Panels.
RTS = most common intercom system in the U.S. Actually stands for Ring – Tip – Sleeve, a type of audio connector. Other intercom system suppliers are Reidel and Clear Com.
Rundown Sheet = a simple review of the script for the TV Production. It breaks the show into "blocks" split by breaks and it lists all the different pieces of the show and what should happen during these pieces (e.g. a graphic will display, or a video tape will be played). This is useful for the crew so that they do not have to read through an entire script during production, they have the show in a simplified form.
Running Time = How long it takes a show to go from start to finish. Often abbreviated TRT (total running time).
RX = receive.
S
SAN (Storage Attached Network) = Storage network that is directly attached to one or more servers most commonly over SCSI or Fiber Channel.
Sandbox = an area of the truck setup with basic workspace, computer cabling, often a keyboard, mouse, and monitor, along with some track lighting. These spaces are intended to be used for whatever necessary ancillary activities, some foreseen, some not, that are required for a particular remote. Sometimes entire B Units are setup to be a sandbox.
Safe area = a term used in television production to describe the areas of the television picture that can be seen on television screens.
Satellite truck = a mobile satellite Earth station typically mounted on a truck chassis as a platform allowing satellite transmission from any location that the vehicle can reach provided a line of site (direct view) to the desired satellite is available.
Satellite television = television delivered by the means of communications satellite and received by a satellite dish and set-top box. In many areas of the world it provides a wide range of channels and services, often to areas that are not serviced by terrestrial or cable providers.
Satellite relay = an active or passive satellite repeater that relays signals between two terminals.
Scoreboard = a large board for publicly displaying the score in a competition, game or match.
Screenburn = Where a permanent mark is burnt into the mask of the TV screen due to prolonged display. Common with sets tuned to one channel for promotional purposes or on ordinary sets from DOGs inserted by broadcasters. Also known as Phosphor burn-in.
SD = Standard Definition
SDI = Serial Digital Interface
SECAM (Séquentiel couleur à mémoire, French for "Sequential Color with Memory”) = A system that was used mostly for French analogue TV transmissions. Instead of AM for color like NTSC and PAL used it used FM and transmitted the two color difference signals separately, every other line.
Senior Video = the video operator charged with maintaining the “look” of all the cameras. He might have multiple assistant video operators to make iris and black levels but senior video ensures that they all match from a color temperature and gamma perspective.
Serial digital interface (SDI) refers to a family of video interfaces standardized by SMPTE.[1] For example, ITU-R BT.656 and SMPTE 259M define digital video interfaces used for broadcast-grade video. A related standard, known as high-definition serial digital interface (HD-SDI), is standardized in SMPTE 292M; this provides a nominal data rate of 1.485 Gbit/s.
Set-top box (STB) or set-top unit (STU) = a device that connects to a television and an external source of signal, turning the signal into content which is then displayed on the television screen.
Set, Shot, and Strike (S3) = A one day remote, where event setup, the event itself, and teardown occurs all in one day.
Shader = This is an archaic term that lives on. Early on cameras were very unstable and would require constant adjustment as lighting changed, or simply as a function of time as equipment heated up, or cooled down when the sun set. One manifestation of this was that the left or right, or top or bottom of the picture would have different video brightness levels. It looked like part of the picture was shaded. The video operator, the correct term today, would make adjustments to even the whole image brightness out.
Shared Resources Trailer (SRT) = A trailer that distributes shared resources among the production trucks supporting a number of rights holders. An example is a weekend of racing at a NASCAR track where one rights holder has Friday Night racing rights, currently Speed Channel, ESPN does Saturday Night Racing, and ESPN, Fox, or Turner alternate between the Sunday main event race. Many of the same sources need to go to, in this case, up to three different sets of production trucks. In addition those sources will need to go the track’s Jumbotron production system and to NASCAR itself who produces an international feed.
SHED (SMPTE Hybrid Elimination Device) = Box that allows a camera to be powered where the camera head is located and eliminates the need to use what is referred to a SMPTE Hybrid cable. SMPTE cable not only has fiber stands but two pairs of 20 gauge copper wires for power. There is also a pair of conductors for data, plus a steel wire for strength. While the SHED doesn’t totally eliminate SMPTE cable, as it still requires a short length of SMPTE cable at the camera and truck ends to connect the camera to the SHED and the truck to the SHED, SHED allows plain old fiber to be used for the vast majority of the distance. With a SHED power can be obtained where the camera is located and data is light multiplexed down the fiber.
Shore Power = Electrical power supplied via normal connection to utility power, as opposed to power supplied by a portable generator.
Shotgun, or Shotgun Microphone = very directional microphone usedin sports to capture sound effects and in cinema production to capturedialog when mounted on a boom or fishpole.
Show Levels = The compliment of equipment and services that a production truck will be expected to handle. Such as how many hard and handheld cameras, how many replay channels, the amount of graphics and audio sources expected.
Show Truck = See Sports Truck
Simulcast = When a broadcaster joins another feed typically produced by a third-party supplier outside their facility either live or in a prerecorded format. For example, a press conference or event that is simultaneously joined by various non-related broadcasters.
Side-by-side = When two separate production trucks cover the same event, such as home and away team coverage. Often one truck is the lead truck and provides multiple feeds to the second truck which aggregates those with sources of its own.
Single-End Audio = See Balanced Audio
Single-mode optical fiber (SMF) (monomode optical fiber, single-mode optical waveguide, or unimode fiber) = an optical fiber designed to carry only a single ray of light (mode). This ray of light often contains a variety of different wavelengths. Although the ray travels parallel to the length of the fiber, it is often called the transverse mode since its electromagnetic vibrations occur perpendicular (transverse) to the length of the fiber.
Single-Phase Power = Single phase is a bit of a misnomer as it was two legs of 120V, each 180 degrees out of phase with one another. Added together they are 240V. This is the type of power most residential customers receive. While a few pieces of equipment might use 240V, everything else is divided up between the two 120V legs. With single phase the two legs are 180 degrees out of phase and if looked at vectorally, they line up in a single line - hence single phase. Also see Three-Phase Power.
Skycam or SpiderCam = the trademarked brandname of a patented, computer-controlled, stabilized, flying camera system. The system, similar to Steadicam, but maneuvered through three dimensions in the open space over a playing area of a stadium or arena by computer-controlled cable-drive system, is responsible for bringing video-game-like camera angles to television sports coverage.
Slo-Mo = Short for Slow-Motion video playback, originally from VTRs, now mainly from video servers.
SMPTE = Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers. One of the standards making organization for motion picture and television production.
SMPTE Hybrid Cable , also SMPTE Fiber = cable connecting the camera to it base station. Comprised of two single mode fibers as well as copper conductors for power and signaling.
Snake = A cable that is comprised of many conductors or a bundling of individual cables into a thick cable that resembles a snake.
Sneaker Net = When files are transferred from one system to another via a thumb drive or other portable media by a human walking.
Sniffer = See Fox and Hound
SNG – Satellite News Gathering. Usually done with a KU Truck. But any satellite link that news uses is considered SNG.
SNR or S/R = Signal to Noise ratio
Sound = a travelling wave which is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.
Soundtrack refers to three related concepts: recorded music accompanying and synchronized to the images of a motion picture, television program or video game; a commercially released soundtrack album of music as featured in the soundtrack of a film or TV show; and the physical area of a film that contains the synchronized recorded sound.
SOT (Sound on Tape) = (Television News) Any video complete with recorded quote, graphics, music or sound intended to be aired as a complete package without voiced commentary.
Soundbite = A small portion (usually one or two sentences) of an audio recording (often an interview) used to illustrate a news story in the words of the interviewee (c.f. a quotation from a politician). See also SOT.
Source = input to a routing switcher
Sponsorship = In the United States, the practice of a company funding the making of a program in order to entertain an audience and sell a product. In the UK, an advertisement inserted between the end-of-part caption and the breakbumper.
Sports Truck = There are a number of differences between a show and sports truck. The production compartment in a show truck will often require more people for a show, as music and art directors and other assistant directors and producers are often present. Since these trucks contain a finite amount of space, the space given to one area must come from another. Thus, show trucks generally take space from the tape/replay compartment to allow for larger audio and production compartments. Entertainment or show productions can generally be accommodated in a sports truck, but sports productions in a show truck can be hampered by the lack of space in the tape compartment. Most trucks are laid out as sports trucks.
Spot = A radio, television commercial or underwriting spot
Spot advertising = A commercial or commercials run in the middle of or between program, sold separately from the program (as opposed to sponsors' messages).
Spatial Resolution = The amount of pixels in a single frame of video. Total pixels is the sum of active horizontal pixels times active vertical lines.
Specialty channel (or speciality channel) = a television channel which consists of programming focused on a single type or targeted at a specific demographic.
Spill Down = In audio mixing the process of taking a complete audio signal, say a 5.1 mix, and breaking it apart to adjust individual channels in that complete signal.
Splitter = Usually refers to a passive audio device that takes one audio source in and provides two or more outputs.
Sports channels are television specialty channels (usually available exclusively through cable and satellite) broadcast sporting events, usually live, and when not broadcasting events, sports news and other related programming.
SSM (Super Slow Motion) = a broadcast industry standard to describe a video processing system that delivers individual frames at high speed, typically 75 frames per second, or a field rate of 150/s. Providing that both a camera system and the recording system are operating at 150/s the replayed signal is of very fine quality, and highly suited for sports broadcasting.
STB = Set-top Box
Stand Up = A commentary or report by a TV correspondent seen on camera, usually at the scene of the action. Used to open, close, or bridge the elements of a report.
Standard-definition television (or SDTV) refers to television systems that have a resolution that meets standards but not considered either enhanced definition or high definition. The term is usually used in reference to digital television, in particular when broadcasting at the same (or similar) resolution as analog systems.
Stem (Audio) = Creating a group of audio channels to be mixed and processed together before becoming part of the final mix. They are also known as sub-mixes, and referred to as being on the same bus.
Streaming media = multimedia that is constantly received by, and normally presented to, an end-user while it is being delivered by a streaming provider (the term "presented" is used in a general sense that includes audio or video playback). The name refers to the delivery method of the medium rather than to the medium itself.
Stick Mic = microphone for hand held use.
Sting = a visual and/or musical punctuation that signals a break between two sections of a program
Submix = See Stems
Subtitles = Text version of a program's dialogue, overlayed on the screen either at broadcast or at reception (often via Teletext or Closed Captioning) for the hearing impaired or for when a speaker is unclear or speaking in a foreign language.
Swag = Stuff We All Get- freebies sometimes given to crew such as hats, tee shirts, jackets ,or tickets
Sync Generator = device used to generate a common reference signal for system timing in video and audio systems. Sophisticated Sync Generator systems can make black burst, tri-level, color bars, test patters, audio tones and audio silence in digital and analog formats. Many can lock to GPS signals to achieve very accurate time stability. Usually found in pairs with an automatic changeover for redundancy.
Sweeps = A period, usually in February, May, July and November, where the ACNielsen Company undertakes audience measurement to record the Nielsen ratings of all shows in all markets with all demographics. This allows networks and local stations to spot surprise hits and unexpected failures. It is also a time when a successful network will try pilot episodes of new shows, whilst a failing network will often put existing successful programs in place of poorly performing shows to boost average ratings.
T
Tactical Fiber = This means that the fiber cable is intended for rugged use in extreme environments and has the ability to be laid down for temporary use and pulled back up again. Even the connectors used, quite rugged themselves, generally have a life of 1000-2000 mating cycles.
Talent = The paid staff who are seen or heard on the air, often the interviewer.
Tape sync = An interview conducted by phone and recorded in both locations, with the two recordings to be mixed later.
TD = See Technical Director
TDC-100 = a device built by Lance Design thast interfaces playback servers with production switcher efficiently. Common in all U.S. mobile units.
Teaser or Cold open = A part of a program played before the title sequence, usually featuring a cliffhanger or prefiguring the plot of the episode to follow.
Tech Power = Truck power is generally divided into two or three areas. Environmental power for air conditioning, tech power for equipment, and sometimes separate utility power for everything else.
Technical Director = Cuts or switches the video portion of the show based on direction from the director. In some situations still, and historically he was in charge of the technical crew, including cameramen, and he was looked on to resolve issues where the production intent wasn’t being met technically.
Telco = Short for the telephone company, either one that provides local phone service, or one that carries voice, data, and video, long distances.
Television (TV) = The transmission of pictures and sound by radio frequency or cable for public reception.
Television news refers to disseminating current events via the medium of television. "News bulletins" or "newscasts" are programs lasting from seconds to hours that provide updates on world, national, regional or local news events. Television news is very image-based, showing video of many of the events that are reported.
Television news channels are television specialty channels which focus on presenting news content.
Television network = a distribution network for television content whereby a central operation provides programming for many television stations.
Television set (usually called a television, TV set, or simply TV) = a device used to view television broadcasts, not to be confused with monitors, which are unable to independently tune into over-the-air broadcasts.
Television standards conversion = the process of changing one type of TV system to another. The most common is from NTSC to PAL or the other way around. This is done so TV programs in one nation may be viewed in a nation with a different standard. The TV video is fed through a Video standards converter device that changes the video to a different video system.
Television studio = an installation in which television or video productions take place, either for live television, for recording live to tape, or for the acquisition of raw footage for postproduction.
Temporal Resolution = The amount of video frames produced every second. SD has temporal resolution of 30, as does 1080i. 720p and 1080p have 60 frames/sec of temporal resolution.
Terrestrial Television = a term which refers to modes of television broadcasting which do not involve satellite transmission or via underground cables.
TGA File Format, often referred to as TARGA File Format, = a raster graphics file format. It was the native format of Truevision Inc.'s TARGA and VISTA boards, which were the first graphic cards for IBM-compatible PCs to support Highcolor/truecolor display. This family of graphic cards was intended for professional computer image synthesis and video editing with PCs; for this reason, usual resolutions of TGA image files match those of the NTSC and PAL video formats. TARGA is an acronym for Truevision Advanced Raster Graphics Adapter; TGA is an initialism for Truevision Graphics Adapter. Today, most people refer to the format as the "TARGA File Format."
Three-Phase Power = Three-phase power is what most large trucks require now to handle the power load. 'Three phase' is just that - three phases of 120VAC. Each phase is 120 degrees out of phase with each other. Vectorally adding these voltages, leg to leg, would produce a voltage of 208V. Generally, trucks spec that each leg be able to supply up to 200 amps. Also see Single-Phase Power.
Tie Lines = Generally cables that have no dedicated use that link one section of a truck to another. Tie lines usually terminate at patch panels or other IO panels.
Tiling = The appearance of large non-congruent blocks on a video display when a digitally generated broadcast (i.e., image) was received by the monitor in an incomplete form. Tiling also occurs when the video signal has degraded or been partially interrupted as it was received by the monitor.
Time code (TC) = a sequence of numeric codes generated at regular intervals by a timing system. Time codes are used extensively for synchronization, and for logging material in recorded media. SOM is also a related term (in the broadcast industry) and stands for 'Start of Message' or 'Start of Media' also known as Time Code (TC) in. Similarly EOM stands for 'End of Message' or 'End of Media' also known as Time Code (TC) out.
Title Safe Area = in television broadcasting, a rectangular area which is far enough in from the four edges, such that text or graphics show neatly: with a margin and without distortion. This is applied against a worst case of on-screen location and display type. Typically corners would require more space from the edges.
Toner = See Fox and Hound
Transition Replay Wipe = The short animated movement, usually from left to right to signify the transition from live pictures to a replay or sequence of replays. The same applies in the reverse direction, from the last replayed item back to live pictures.
Transponder = A receiver/transmitter combination in a satellite. A satellite can have many transponders. Multiple programs can use the same transponder simultaneously.
Transport Stream = Constant stream of packetized video and audio, usually compressed, wrapped with metadata that allows a set top box or other decoder to unwrap the media and play it. Transport streams can be real-time, or slower and faster than real-time.
Triaxial cable = A specialized form of coaxial cable, circular in cross-section and consisting of (a) a center conductor, often a solid wire but sometimes braided.
Twins = A two trailer unit that operates as a single production facility. Twins can’t operate by themselves, as many A units can do without their B unit. One trailer usually has a very large control room and graphics while the second trailer will house audio, replay, video, and engineering. Sometimes these units can be considered “Triplets” as they sometimes have a third unit that will handle audio effects, edit bays, and sideline camera platforms. They can even become “Quads”, where a D unit handles enhance or virtual graphics, transmission encoding and a second control room for the Pre-game show. As you add more tools for storytelling you necessitate more operator workstations.
Turn Around = See Gender Bender
Twisted pair cabling = a form of wiring in which two conductors (the forward and return conductors of a single circuit) are twisted together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources; for instance, electromagnetic radiation from unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables, and crosstalk between neighboring pairs.
Tub = Slang for the frame in a rack that houses either the video switcher, the intercom, or the video or audio routers.
Twofer = lighting power cable with one male plug, two female receptacles, a Y-Cord.
TX = transmit
U
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) = Frequencies between 300 MHz (wavelength 1 meter) and 3.0 GHz (wavelength 10 centimetres), used for television broadcasting.
Ultra-HD = consumer term for 4k
Unilateral Signal = an individual or single transmission path intended for a specific destination or territory. Unilateral Broadcasters is also a term given to RHB as well as unilateral facilities for services and equipment they may need.
Upconversion = Typically used to increase scan lines on SD video so content can be viewed or processed in a higher resolution environment. Quality is not improved, but scan lines are added to permit a suitable viewing experience in a higher resolution environment.
Uplink = The portion of a communications link used for the transmission of signals from an Earth terminal to a satellite or to an airborne platform. An uplink is the inverse of a downlink.
UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply) = Used for critical broadcast or event deliveries when the primary source of electricity is supplied from the local grid. Should there be a power failure, the UPS protects the demand, first by a series of heavy duty batteries to supplement the power and then by electricity from a diesel generator. The process is a seamless task that will not disturb or interrupt the power supply for the broadcast or live event operation.
Utilities (also known as Riggers in the U.K.) = they handle the initial setup on a remote, building camera platforms and running cables. Utilities are a combination carpenter, electrician, jack-of-all-trades and miracle worker when getting the production setup. During production, they often become Grips by assist camera operators with camera movement, handling cables, driving sideline carts and operating specialized camera mounts.
V
VandA = A feed containing video and audio.
VBI (Vertical Blanking Interval) = The blank area out of sight at the top and bottom of a television picture that allows the raster gun to reset. The space created is often used for Teletext and other services.
VBR= variable bit rate
Vectorscope = display and measurement device designed for the analysis of the color components of an analog video signal. So loved by video engineers that there are digital versions that display the color components of a digital or HD signal in the very familiar analog format.
VCR = Video Cassette Recorder. Now being phased out and replaced by DVD recorders and PVRs
VOD = Video On Demand
VHF = Very High Frequency
Frequencies from 30 MHz (wavelength 10 m) to 300 MHz (wavelength 1 m), used for radio and television broadcasting.
Video = the technology of electronically capturing, recording, processing, storing, transmitting, and reconstructing a sequence of still images representing scenes in motion.
Video camera = a camera used for electronic motion picture acquisition, initially developed by the television industry but now common in other applications as well.
Video clips = short clips of video, usually part of a longer piece. In digital format are often found on the internet. The term is also more loosely used to mean any short video less than the length of a traditional television programme.
Video compression refers to reducing the quantity of data used to represent digital video images, and is a combination of spatial image compression and temporal motion compensation. Video compression is an example of the concept of source coding in Information theory. This article deals with its applications: compressed video can effectively reduce the bandwidth required to transmit video via terrestrial broadcast, via cable TV, or via satellite TV services.
Video Control = The task of video controller is the same as the gatekeepers. The video controller will control that the gates are passed correctly.
Video monitor also called a broadcast monitor, broadcast reference monitor or just reference monitor, is a device similar to a television, used to monitor the output of a video-generating device, such as a media playout server, IRD, video camera, VCR, or DVD player.
Video On Demand (VOD) systems allow users to select and watch/listen to video content on demand. VOD systems either stream content through a set-top box, allowing viewing in real time, or download it to a device such as a computer, digital video recorder, personal video recorder or portable media player for viewing at any time. The majority of cable- and telco-based television providers offer both VOD streaming, such as pay-per-view, whereby a user buys or selects a movie or television program and it begins to play on the television set almost instantaneously, or downloading to a DVR rented from the provider, for viewing in the future.
Video podcast = a term used for the online delivery of video on demand video clip content. The term is used to distinguish between podcasts which most commonly contain audio files and those referring to the distribution of video where the RSS feed is used as a non-linear TV channel to which consumers can subscribe using a PC, TV, set-top box, media center or mobile multimedia device. Web television series are often distributed as video podcasts.
Video server = a computer based device (also called a 'host') dedicated to delivering video. Being multi-application devices, a video server is designed for one purpose; provisioning video, often for broadcasters. A professional grade video server records, stores, and plays back multiple streams of video without any degradation in the video signal.
Videotape = a means of recording images and sound onto magnetic tape as opposed to movie film.
Video Tape Recorder (VTR) = a tape recorder that can record video material. The video cassette recorder (VCR), where the videotape is enclosed in a user-friendly videocassette shell, is the most familiar type of VTR known to consumers.
VITC = Vertical Interval Time Code
Vision mixer (also called video switcher, video mixer or production switcher) = a device used to select between several different video sources and in some cases composite (mix) video sources together and add special effects. This is similar to what a mixing console does for audio.
VNR A Video News Release. = The television equivalent of a news release.
VO (Video Only) = (U.K. Television News) Video without commentary intended to be aired along with a news correspondent reading the news story.
VO (Voice Over) = The term voice-over refers to a production technique where a non-diegetic voice is broadcast live or pre-recorded in radio, television, film, theatre and/or presentation. The voice-over may be spoken by someone who also appears on-screen in other segments or it may be performed by a specialist. Voice-over is also commonly referred to as "off camera" commentary. Normally found on channel 1.
VOIP (Voice Over IP or Video Over IP) = Used for both voice and video but historically has generally referred to voice. Generally using IT techniques to transmit voice or video.
Voxel (volumetric pixel or, more correctly, Volumetric Picture Element) a volume element, representing a value on a regular grid in three dimensional space. This is analogous to a pixel, which represents 2D image data in a bitmap (which is sometimes referred to as a pixmap). As with pixels in a bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (their coordinates) explicitly encoded along with their values. Instead, the position of a voxel is inferred based upon its position relative to other voxels.
VTR (Video Tape Recorder) = a method of recording television pictures by electromagnetic pulses on a sensitized plastic strip.
VU (Volume Unit) = Used in conjunction with analog audio. Although measured in dB VU is a relative measure as 0 VU over the years has been reference to +3, +4, and +6 dBm. Analog levels will be a function of whether the analog audio is balanced or not. 0 VU has historically been the target to match when setting the average peak levels of analog audio.
Vyvx = Early fiber landlines provider, now part of Level 3 Communications. Vyvx is not an acronym, the letters were randomly picked.
W
Watermark = A common practice of displaying a company's logo during a television broadcast, typically a translucent image in the right hand bottom corner. (See also Bug and DOG)
Waveform Monitor = device for displaying, measuring and in sophisticated models, analyzing the video signal. There are versions for analog signals and digital signals. Some models can store and list the errors received in the signals.
Webcams = video capturing devices connected to computers or computer networks, often using USB or, if they connect to networks, ethernet or Wi-Fi. They are well known for their low manufacturing costs and flexible applications.
Webcast = a media file distributed over the Internet using streaming media technology to distribute a single content source to many simultaneous listeners/viewers. A webcast may either be distributed live or on demand. Essentially, webcasting is "broadcasting" over the Internet.
Web television (Web TV) = an emerging genre of digital entertainment that is distinct from traditional broadcast television. Delivered originally online via broadband and mobile networks, Web television shows, or Web series, are short-form in nature (2-9 minutes per episode), episodic, and produced in seasons.
Wendy = A large carpeted wedge used to display items for shooting.
White Noise = See pink noise
Wind Screen/Sock = Protection placed over microphone to limit wind noise.
Whole Cut Signal = See Keying - Video
World Feed = Generic feed, usually a clean feed, that covers an event without any particular emphasis on any one countries participation. Many broadcaster from a particular country will add cameras, graphics, and on air talent to personalize the coverage for their audience.
Wrapper = Additional data added to a file that identifies the video and audio attributes contained in a file.
Wipe = a gradual spatial transition from one image to another. One image is replaced by another with a distinct edge that forms a shape. A simple edge, an expanding circle, or the turning of a page are all examples.
Wireless communication = the transfer of information over a distance without the use of electrical conductors or "wires." The distances involved may be short (a few meters as in television remote control) or long (thousands or millions of kilometers for radio communications). When the context is clear, the term is often shortened to "wireless."
Wireless communication is generally considered to be a branch of telecommunications.
WirelessHD = an industry-led effort to define a specification for the next generation wireless digital network interface for wireless high-definition signal transmission for consumer electronics products.
Wireless access point (WAP or AP) = a device that allows wireless communication devices to connect to a wireless network using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or related standards. The WAP usually connects to a wired network, and can relay data between the wireless devices (such as computers or printers) and wired devices on the network.
X
XLR = standard connector for audio, most commonly with three pins or contact points. Four and five pin versions are used for intercom headsets and multi-channel microphones. Cannon Electric invented the connector and made it part of its "X" series or connectors. Because of its locking mechanism the "L" was added, and the fact that it has rubber insulation resulted in the final "R" designation.
XM Satellite Radio = An American satellite radio platform, merged with Sirrius.
Y
Y = Luminance in many color models used for television broadcast, such as YIQ and YUV.
Yellow Jackets = Industry standard protective cable trays, used for indoor and outdoor use to identify a cable path in a safe and protective jacket. Usually positioned at ground level, where the cable path crosses an area also used for public access.
YouTube = a video sharing website on which users can upload and share videos, and view them in MPEG-4 format.
Z
Zoom = To go from a long shot to a close-up (or vice versa) with the camera.
Zoom lens = a mechanical assembly of lens elements with the ability to vary its focal length (and thus angle of view), as opposed to a fixed focal length (FFL) lens. They are commonly used with still, video, motion picture cameras, projectors, some binoculars, microscopes, telescopes, telescopic sights, and other optical instruments.
Zooming = a method of decreasing (narrowing) the apparent angle of view of a digital photographic or video image. Digital zoom is accomplished by cropping an image down to a centered area with the same aspect ratio as the original, and usually also interpolating the result back up to the pixel dimensions of the original. It is accomplished electronically, without any adjustment of the camera's optics, and no optical resolution is gained in the process.